Sunday, December 25, 2011
Mic Preamplifier Circuit based TLC251
Here the schematic diagram of mic preamplifier which build based on operational amplifier TC251. The TLC251 is operating in low bias. The circuit works with only 1.5 V supply draws electric current of only 10 mA, so the battery operation will be prefered. Circuit frequency response is 3dB, 27 Hz to 4.8 kHz.
Frequency Response:
The TLC251 are low-cost, low-power programmable operational amplifiers designed to operate with single or dual power supplies. Because the input common-mode range extends to the negative rail and the power consumption is very low, this chip is ideally suited for battery-powered or energy-conserving applications. A bias-select pin can be used to program one of three ac performance and power-dissipation levels to suit the application. The series features operation down to a 1.4V supply and is stable at unity gain.
Download the TLC251 datasheet document from the following link:
» Download link
ReadMore[..]
Frequency Response:
The TLC251 are low-cost, low-power programmable operational amplifiers designed to operate with single or dual power supplies. Because the input common-mode range extends to the negative rail and the power consumption is very low, this chip is ideally suited for battery-powered or energy-conserving applications. A bias-select pin can be used to program one of three ac performance and power-dissipation levels to suit the application. The series features operation down to a 1.4V supply and is stable at unity gain.
Download the TLC251 datasheet document from the following link:
» Download link
Sunday, December 18, 2011
Stereo Tube Power Amplifier Schematic
This is the circuit diagram of stereo tube power amplifier. It applies 3 types of tube that are 2 6SF5 GT high-mu triodes, 1 5Y3 GT vacuum rectifier, and 2 6K6 power beam amplifiers. The Audio input can be from any two-channel line level device such as a television, CD player, or VCR. It is of the tube type, using only 5 tubes total with no more than about 45 Watts power consumption from the outlet.
Components List:
R1,R10,R13 = 2.2M Ohm Potensiometer
R2 = 470K Ohm
R3 = 1M Ohm
R4 = 220K Ohm
R5 = 330 Ohm 2W Resistor
R6 = 220K Ohm
R7 = 2.2M Ohm
R8 = 1M Ohm
R9 = 720 Ohm 20W Resistor
R11 = 33K Ohm
R12 = 22K Ohm
C1,C9 = 4nF 400V Capacitor
C2 = 50nF 600V Capacitor
C3 = 20uF/25V
C4 = 10nF 400V Capacitor
C5 = 200pF 400V Ceramic Disc Capacitor
C6,C7 = 15uF 450V Capacitor
C8 = 15uF 400V Capacitor
T1 = 117V Primary, 350VCT Secondary, 6.3V Secondary, 6.3V Secondary
T2 = 7600 Ohm Primary, 4 or 8 Ohm Secondary
SW1 = SPST Switch
SP1,SP2 = 12" or smaller, 4 or 8 ohm speakers
MISC = 5 tube sockets, 2 RCA jacks, PC board or chassis, wire, knobs, etc.
Stereo Tube Power Amplifier Circuit Notes:
- C8 is for radio interference suppression and may be omitted.
- The 6V6 GT tube may be substituted for the 6K6 to lower power requirements.
- The 5Y3 GT tube should be mounted in a vertical position and be well ventilated. The 6K6 and 6SF5 tubes can be mounted in any position.
- The power supply portion of this unit may be used for anything requiring 290-320v DC up to about 3 amperes.
- Controls should have an audio taper.
Saturday, December 3, 2011
BA5417 Stereo Power Amplifier
Setup and dealing of this stereo power amplifier circuit is somewhat similar to the BA5406 based mostly stereo amplifier circuit revealed previously. C10 and C11 are DC decoupling capacitors that block any DC level present in the input signals. C2 and C6 couples the amplifiers left and right power outputs to the corresponding loud speakers. C1 and C5 are bootstrap capacitors.
Bootstrapping is a technique during which a portion of the amplifiers is taken and applied to the input. The prime objective of bootstrapping is to boost the input impedance. Networks R1,C3 and R2,C7 are meant for improving the high frequency stability of the circuit. C4 is the power supply filter capacitor. S1 is the standby switch. C8 is a filter capacitor. R3 and R4 sets the gain of the left and right channels of the amplifier in conjunction with the 39K internal feedback resistors.
Bootstrapping is a technique during which a portion of the amplifiers is taken and applied to the input. The prime objective of bootstrapping is to boost the input impedance. Networks R1,C3 and R2,C7 are meant for improving the high frequency stability of the circuit. C4 is the power supply filter capacitor. S1 is the standby switch. C8 is a filter capacitor. R3 and R4 sets the gain of the left and right channels of the amplifier in conjunction with the 39K internal feedback resistors.
Wednesday, November 30, 2011
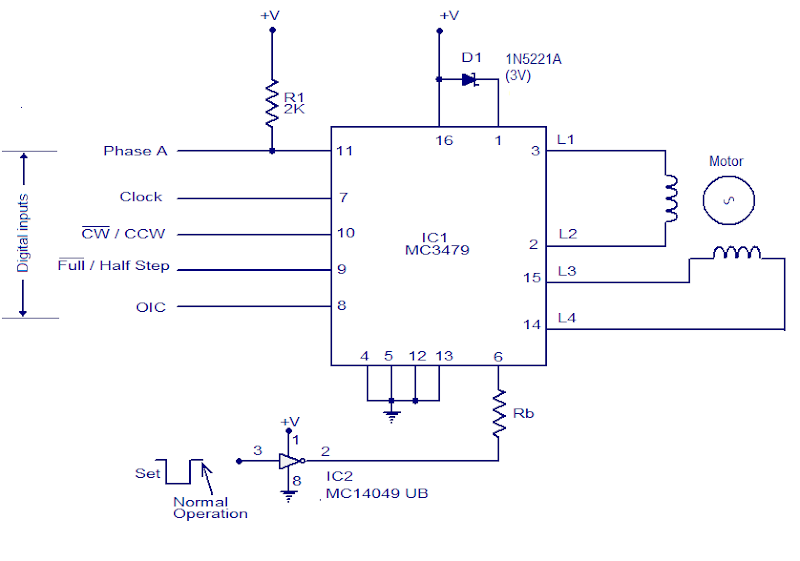
MC3479 Stepper Motor Driver
The circuit diagram is given here is a motor controller driver using the Motorola MC3479. The MC3479 is designed specifically for driving a stepper motor phase 2 in bipolar mode and is available in standard DIP and surface mount IC packages.The is compatible with TTL and CMOS and has selectable HI / LOW output impedance .
The output can deliver up to 350 mA each of the two coils of a stepper motor 2 phases. The change of output state occurs in the low to high transition of the input clock pulse. The new output will depend on the exit of age and state of the digital inputs. The output L1 to L4 are the results of high currents, which when connected to a stepper motor a two-phase full-bridge two formations.
Resistors R1 and Rb, Zener diode D1 and IC2 MC14049UB are additional components that are used in the circuit. R1 is an uprising and resistance Rb is used to set the maximum output sink. Zener diode D1 provides back emf protection.
The output can deliver up to 350 mA each of the two coils of a stepper motor 2 phases. The change of output state occurs in the low to high transition of the input clock pulse. The new output will depend on the exit of age and state of the digital inputs. The output L1 to L4 are the results of high currents, which when connected to a stepper motor a two-phase full-bridge two formations.
Resistors R1 and Rb, Zener diode D1 and IC2 MC14049UB are additional components that are used in the circuit. R1 is an uprising and resistance Rb is used to set the maximum output sink. Zener diode D1 provides back emf protection.
Mini FM Transmitter using MAX2606

With MAX2606 you can make a Mini mono FM transmitter. It is built with MAX2606 and covers at least 20 meters with 1.5 m length of copper wire antenna. You can use this transmitter as an oscillator, but change the 1000pF capacitor of the antenna with 15pF.
MAX2606 transmitter output power is-10dBm, which means something around 100uW (micro-watts) = 0.0001. Of course this is very low, so it is recommended the use of auxiliary power amplifier, if you want to build a more powerful transmitter based on MAX2606. You can find a power amplifier in a few fm electroschematics.com so please use the search box.
MAX2606 transmitter output power is-10dBm, which means something around 100uW (micro-watts) = 0.0001. Of course this is very low, so it is recommended the use of auxiliary power amplifier, if you want to build a more powerful transmitter based on MAX2606. You can find a power amplifier in a few fm electroschematics.com so please use the search box.
Monday, November 28, 2011
3-Level Audio Power Indicator

This circuit is designed to indicate the power level output of any audio amplifier. It's simple, portable, and displays three power levels can be adjusted to any desired value. For a standard power amplifier hi-fi stereo, the output values suggested are:
- D5 illuminates at 2W
- D4 illuminates at 12.5W
- D3 illuminates at 24.5W
9 Volt Portable Mixer Circuit

The objective of this project was to design a small portable mixer supplied by a 9V PP3 battery, keeping performance quality. The mixer is formed assembling three main modules that can vary in number and / or willingness to adapt to the needs of all.
The three modules are:
Amplifier Input Module: a low-noise circuit equipped with a variable voltage gain (10 - 100) pre-set, primarily intended as input to high-quality microphone is also suitable for line level input on .
Tone Control Module: One of three bands (Low, Mid, Treble) tone control circuit provides unity gain when the controls are set flat frequency response. Can be inserted after one or more modules of the amplifier and / or after the main mixer amplifiers.
Main Module mixer amplifier, a music circuit incorporating two virtual mixing earth and shows the connection of a Master Fader and Pan-Pot.
The three modules are:
Amplifier Input Module: a low-noise circuit equipped with a variable voltage gain (10 - 100) pre-set, primarily intended as input to high-quality microphone is also suitable for line level input on .
Tone Control Module: One of three bands (Low, Mid, Treble) tone control circuit provides unity gain when the controls are set flat frequency response. Can be inserted after one or more modules of the amplifier and / or after the main mixer amplifiers.
Main Module mixer amplifier, a music circuit incorporating two virtual mixing earth and shows the connection of a Master Fader and Pan-Pot.
Sunday, November 27, 2011
10W Audio Amplifier with Bass-boost

This Audio Amplifier design is based on the audio amplifier 18 watts, and was developed primarily to meet the requests of correspondents unable to locate the chip TLE2141C. It uses the NE5532 Dual IC wide, but obviously, its power output will be written in the 9.5 - 11.5W range, as the supply rails can not exceed ± 18V.
As amplifiers of this type are often used to drive small loudspeaker cabinets, the bass frequency range is rather sacrificed. Therefore, a Bass Boost control was inserted in the amplifier feedback loop, in order to overcome this problem, without loss of quality. The low elevation curve can reach a maximum of 16.4 dB @ 50Hz. In any case, even when the bass control is turned fully counterclockwise, the amplifier's frequency response curve shows a gentle rise: 0.8 dB at 400 Hz, 4.7 dB at 100 Hz and 6 dB at 50 Hz (referred to 1 kHz).
As amplifiers of this type are often used to drive small loudspeaker cabinets, the bass frequency range is rather sacrificed. Therefore, a Bass Boost control was inserted in the amplifier feedback loop, in order to overcome this problem, without loss of quality. The low elevation curve can reach a maximum of 16.4 dB @ 50Hz. In any case, even when the bass control is turned fully counterclockwise, the amplifier's frequency response curve shows a gentle rise: 0.8 dB at 400 Hz, 4.7 dB at 100 Hz and 6 dB at 50 Hz (referred to 1 kHz).
140mW Headphone Amplifier
Those who want to listen privately to your music program should add this headphone amplifier in the chain of modular preamp. The circuit is kept as simple as possible consistent with high quality performance. This was achieved by using two NE5532 operational amplifiers on a circuit where IC1B is the "master" amplifier in the cable joint inversion of configuration is not already used in the amplifier's control center line. IC1A is the "slave" of the amplifier and is configured as a unity gain buffer: parallel amplifiers to increase the output current capacity of the circuit.
Two headphone outputs are provided by J3 and J4.
The AC gain of the amplifier was deliberately kept low because this module is intended to be connected after the Control Center module, which provides sufficient gain to drive the power amplifier. If you intend to use the headphone amplifier as a standalone device, an AC higher gain may be necessary to cope with a CD player or tuner output. This is achieved by reducing the value of R1 to 1K5. Thus AC gain of 9 is obtained, more than enough for the purpose.
Unlike the two ICs 15V positive and negative regulator used in other modules of this preamp, two devices were used instead of 9V. This is because the NE5532 automatically limits the output voltage at very low loads as 32 Ohm so that the output amplitude of the amplified signal remains the same, whether the circuit is powered by ± 15V to ± 9V. The choice of a source of ± 9 V allows lower power dissipation and better performance of the amplifier near the cutoff point.
The input jack of this amplifier must be connected to the output module main control center. As this output is usually reserved for driving the power amplifier, a second connection (J2) connected in parallel to J1 is provided for this purpose.
As with the other modules in this series, each electronic card can be fitted in a standard: Hammond extruded aluminum cases are well suited to accommodate the tables in this preamp. In particular, instances of size 16 x 10.3 x 5.3 cm or 22 x 10.3 x 5.3 cm look very good when stacked. See below an example of the possible arrangement of the front and back of this module.
Two headphone outputs are provided by J3 and J4.
The AC gain of the amplifier was deliberately kept low because this module is intended to be connected after the Control Center module, which provides sufficient gain to drive the power amplifier. If you intend to use the headphone amplifier as a standalone device, an AC higher gain may be necessary to cope with a CD player or tuner output. This is achieved by reducing the value of R1 to 1K5. Thus AC gain of 9 is obtained, more than enough for the purpose.
Unlike the two ICs 15V positive and negative regulator used in other modules of this preamp, two devices were used instead of 9V. This is because the NE5532 automatically limits the output voltage at very low loads as 32 Ohm so that the output amplitude of the amplified signal remains the same, whether the circuit is powered by ± 15V to ± 9V. The choice of a source of ± 9 V allows lower power dissipation and better performance of the amplifier near the cutoff point.
The input jack of this amplifier must be connected to the output module main control center. As this output is usually reserved for driving the power amplifier, a second connection (J2) connected in parallel to J1 is provided for this purpose.
As with the other modules in this series, each electronic card can be fitted in a standard: Hammond extruded aluminum cases are well suited to accommodate the tables in this preamp. In particular, instances of size 16 x 10.3 x 5.3 cm or 22 x 10.3 x 5.3 cm look very good when stacked. See below an example of the possible arrangement of the front and back of this module.
Saturday, November 26, 2011
144 MHz Simple RF Detector Circuit

This simple circuit helps you sniff out RF radiation from your transmitter, improper joints, a broken wire or poor equipment with RF shielding. The tester is designed for the radio band amateur 2 meter (144-146 MHz in Europe). The instrument has a reading of 4-step LED and an audible alarm for high voltage radiation. The RF signal is received by an antenna and made to resonate by C1-L1. After rectification by the diode D1, the signal is fed to a two transistor Darlington amplifier HighGain, T2-T3. Assuming a 10-inch telescoping antenna using the RF level scale established for the LEDs is as follows:
When all the LEDs light, the (optional) UM66 sound / melody generator chip (IC1) also operates and provides an audible alarm. By changing the zener diode values of D2, D4, D6 and D8, the step size and duration of the instrument may change as needed. To operate in other bands of ham or PMR, simply change the network-L1 C1 resonance.
For example, a transceiver 5 watt handheld equipped with a telescoping half-wave antenna (G = 3.5 dBd), there is an ERP (Effective Radiated Power) of just 10 watts and an emf of more than 8 volts near the head. Inductor L1 consists of 2.5 turns of 20 SWG (approximately 1 mm in diameter) enameled copper wire. The inner diameter is approximately 7 mm and no core is used.
Trimmer capacitor C1 associates is adjusted for the greatest number of LEDs to light at a relatively low fieldstrength position for a 2 m transceiver 145 MHz transmission. The tester is powered by a 9 V battery and consumes about 15 mA when all LEDs are on. Must be enclosed in a metal box.
When all the LEDs light, the (optional) UM66 sound / melody generator chip (IC1) also operates and provides an audible alarm. By changing the zener diode values of D2, D4, D6 and D8, the step size and duration of the instrument may change as needed. To operate in other bands of ham or PMR, simply change the network-L1 C1 resonance.
For example, a transceiver 5 watt handheld equipped with a telescoping half-wave antenna (G = 3.5 dBd), there is an ERP (Effective Radiated Power) of just 10 watts and an emf of more than 8 volts near the head. Inductor L1 consists of 2.5 turns of 20 SWG (approximately 1 mm in diameter) enameled copper wire. The inner diameter is approximately 7 mm and no core is used.
Trimmer capacitor C1 associates is adjusted for the greatest number of LEDs to light at a relatively low fieldstrength position for a 2 m transceiver 145 MHz transmission. The tester is powered by a 9 V battery and consumes about 15 mA when all LEDs are on. Must be enclosed in a metal box.
50W TDA1514 Hi Fi audio amplifier

TDA1514 is a hi fi audio amplifier may output of 50W of sound. The power supply is 10V and 30V. Can be used as an amplifier at home.
The integrated circuit TDA1514 power amplifier is a high fidelity for use as a basic component in applications of radio, television and other audio. The TDA 1514 is fully protected circuit, also has a mute function that can be arranged for a period after the ignition delay time set by external components. The device is designed to power symmetric, but asymmetric source can also be used. For stereo amplifier configuration uses two identical circuits.
Friday, November 25, 2011
AN7415 FM Stereo Demodulator
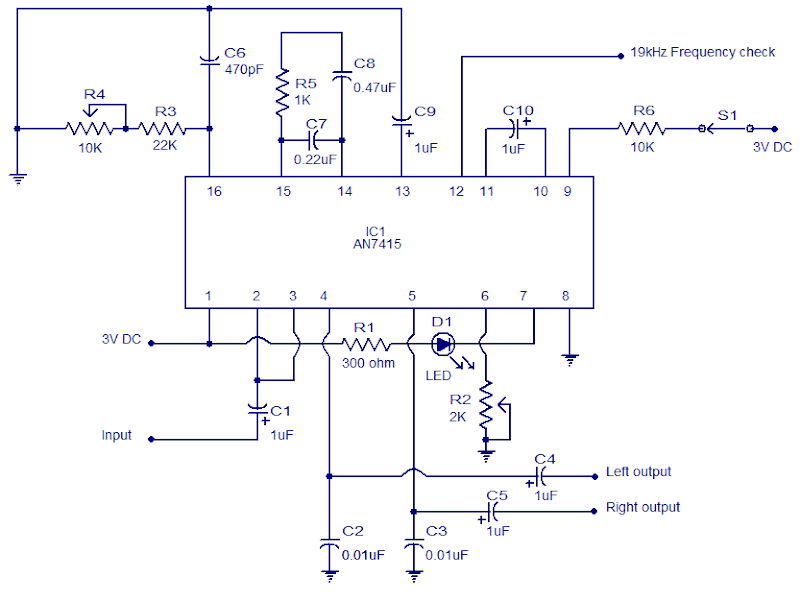
The circuit shown is a stereo FM PLL demodulator designed based on the AN7415. C1 is the input coupling capacitor to block any DC voltage present on the multiplexed input signal. LED D1 is an LED and R1 is the current limiting resistor. C4 and C5 are DC decoupling capacitors to the output channels left and right. C2 and C3 are bypass capacitors for noise output channels left and right. POT R2 can be used to adjust the separation between channels.
The resistor R5 and capacitors C7 and C8 form a network of low-pass filter for the internal DC amplifier circuit (see block diagram AN7415). C10 is a filter capacitor for the internal amplifier circuit Schmitt trigger IC. C9 is a filter capacitor for the circuit wave surge inside the AN7415. Resistor R3, R4 and capacitor C6 POT set the time constant of internal VCO circuit. Therefore POT R4 can be used to adjust the frequency of the VCO. A control signal 19KHz frequency is available in 12 pin IC. The switch S1 can be used to activate and deactivate the forced mono.
The resistor R5 and capacitors C7 and C8 form a network of low-pass filter for the internal DC amplifier circuit (see block diagram AN7415). C10 is a filter capacitor for the internal amplifier circuit Schmitt trigger IC. C9 is a filter capacitor for the circuit wave surge inside the AN7415. Resistor R3, R4 and capacitor C6 POT set the time constant of internal VCO circuit. Therefore POT R4 can be used to adjust the frequency of the VCO. A control signal 19KHz frequency is available in 12 pin IC. The switch S1 can be used to activate and deactivate the forced mono.
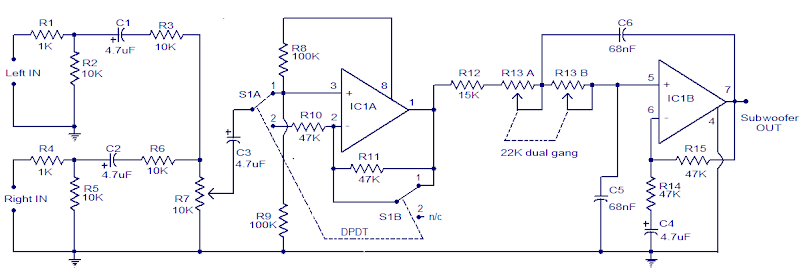
12V DC Car Simple Subwoofer Filter
Here is the circuit diagram of a simple subwoofer filter that can be operated from a 12V DC supply. This circuit is very useful in car subwoofer applications. The circuit is simply a low pass filter whose pass frequency can be adjusted between 60 and 160 Hz.
The circuit is designed around the dual TL072 IC BIFET. Outside the two operational amplifiers in the chip, IC1A is connected as a buffer. The audio inputs left and right after the mixture is fed to the input of the switch S1 IC1A with bipolar. Switch S1 is the phase control switch that can be used to make the subwoofer in phase with the other speakers. When S1 is in position 2, 180 degrees of phase change induced.POT R7 can be used to control the level. IC1B a low pass filter whose pass frequency can be controlled by adjusting the dual band POT R13.
Tuesday, November 22, 2011
12 LED VU Meter Circuit
Here the 12 LED VU meter circuit. This is a simple visual indication of the audio level signals, adaptive to various user needs. Can be adapted to different input levels, adjustable by trimmer TR1 (state) - TR2 (Gain), then rectified by diodes D1-D2 (standard negative mark-recovery periods) and driven in the main circuit indication, consisting of the diodes D3 up to D13, transistors Q2-Q13 and materials that exist around them.
The visual indicator is taken from the series of diodes LED LD1-13. Each Led illuminates when the level changed during about 0,65 V. The power requirements are 100 ma full term. We can add as many steps we want LED, always assuming the power where you need the new LED.
Components List
| R1 = 47Kohm R2,3 = 1Mohm R4,R7 = 1Kohm R5 = 100ohm R6 = 18Kohm R9,11,13,15,17 = 560ohm R19,21,23,25,27 = 560ohm R29,31 = 560ohm R8,10,12,14 = 4.7Kohm R16,18,20,22 = 4.7Kohm R24,26,28,30 = 4.7Kohm C1 = 10uF/25V C2 = 100nF/100V MKT C3 = 4.7uF/25V | C4 = 4.7uF/25V C5 = 10uF/25V C6 = 47uF/25V C7-8 = 100nF/100V TR1 = 100Kohm Trimmer TR2 = 4.7Kohm Trimmer LD1 until LD7 = LED Green LD8,LD9,LD10 = LED Yellow LD11,LD12,LD13 = LED Red D1 until D13 = 1N4148 Q1 until Q13 = BC550C - BC549B IC1 = TL071 IC2 = 7812 [With Heatsink] All Resistors is 1/4W 1 -5% |
12 LED VU Meter Circuit source page: users.otenet.gr
Thursday, November 17, 2011
FanTemperature Controller circuit
This FanTemperature Controller circuit design technique to adopt a more ancient as its objective is to vary the fan speed in relation to temperature with a fraction of counting and avoid using special-purpose integrated circuits, often difficult to obtain.
R3-R1-R4 and P1 are connected as a Wheatstone bridge in which R3-R4 generates a fixed two-thirds of the supply of "reference" voltage, P1-R1 generates a temperature-sensitive "variable" power and Q1 is used as a balanced bridge detector.
P1 is adjusted so that the "reference" stress "variable" is equal to a temperature just below the critical value necessary, and under the base of Q1 and the condition of the issuer are located in the same tensions and Q1 cut. When the temperature rises above this R1 "balance" the value of P1-R1 voltage falls below the "reference" value, so that Q1 is polarized, pulse charging C1.
This is because the circuit is supplied by a 100 Hz half-wave voltage from the mains supply by means of the D3-D6 diode bridge without filter capacitors and fixed to 18V by Zener diode D1 and R9. Therefore the supply of 18 volt DC circuit is not true, but it has a trapezoidal shape instead. C1 provides a variable lag phase pulse train related to temperature and synchronized with the mains "zero voltage" point of each half cycle, resulting in minimal change RFI SCR. Q2 and Q3 form a firing device, which generates a short pulse suitable for driving the SCR.
Wednesday, November 16, 2011
87-108MHz FM Wireless Microphone

This FM wireless microphone is easy to build and has a useful range of transmission (over 300 meters outdoors). Despite its small number of components and an operating voltage of 3V to easily penetrate over three floors of an apartment building. You can tune anywhere on the FM band (87-108MHz) and its transmissions can be picked up at any point of view of the FM receiver.
The coil (L1) should be approximately 3 mm in diameter, 5 turns 0.61 mm copper wire. You can vary the Tx frequency by simply adjusting the distance between the coils. The antenna should be a half wavelength or quarter-time (100 MHz, 150 cm or 75 cm).
Parts list:
The coil (L1) should be approximately 3 mm in diameter, 5 turns 0.61 mm copper wire. You can vary the Tx frequency by simply adjusting the distance between the coils. The antenna should be a half wavelength or quarter-time (100 MHz, 150 cm or 75 cm).
Parts list:
- T1,T2,T3: 2N2222 transistor
- R1: 10k 5%
- R2: 33k lin.
- R3: 12k 5%
- R4: 5.6k 5%
- R5: 2.2k 5%
- R6,R8: 47k 5%
- R7: 470 ohms 5%
- R9: 180 ohms 5%
- C1,C2: 47nF
- C3: 1nF
- C4: 33pF
- C5: 5.6pF
- C6: 8.2pF
- C7: 10nf
- L1: 3mm in diameter with 5 turns 0.61 mm copper wire
- K1: SPDT toggle switch
- Other parts: 2 AA battery holder, Electret microphone, antenna wire
Saturday, November 12, 2011
2-Way Active Crossover Circuit
This is the schematic diagram of 2-way active crossover circuit. The "active" word means that the circuit use active component and need power supply to work. Take a note that the input of this circuit is not connected to the output of power amplifier. This crossover circuit module must be placed before the amplifier circuit. The "Low Out" output connected to a power amplifier and the low speaker [Woofer], while the "High Out" output is drive the power amplifier of high speaker [Tweeter].
Parts List
R1 = 100Kohms
R2,3,4,5,6 = 37.5ohms [33K+4.7K]
R7 = 75Kohms[150K//150K
R8 = N.C
R9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16 = 10Kohms
R17,18 = 47Kohms
R19,20 = 47ohms
C1 = 4.7uF/100V MKT
C2,3,4,5,6,7,12,13 = 1nF 100V MKT
C8,9,10,11,14,15 = 100nF 100V MKT
C16 = 2.2uF/100V MKT
C17 = 470nF 100V MKT
C18,19 = 47uF/25V
J1,2,3 = 2pin conn. 2.54mm pin step
J4 = 3pin conn. 2.54mm pin step
IC1,2,3 = NE5532 , TL072
TR1 = 100Kohms trim. or pot.
TR2,3 = 47Kohms trim. or pot.
All the Resistors is 1,2% 1/4W metal film
Circuit Source: 2-Way Active Crossover Circuit with Linear Phase Response
Wednesday, November 2, 2011
7 Segment Display Counter based 74LS90
 Here is a 7 segment counter circuit based on IC 74LS90 TTL.This can be used in conjunction with several circuits where a counter to show the progress adds a little more attractive. This circuit accepts any TTL compatible logic signal, and can be extended easily.
Here is a 7 segment counter circuit based on IC 74LS90 TTL.This can be used in conjunction with several circuits where a counter to show the progress adds a little more attractive. This circuit accepts any TTL compatible logic signal, and can be extended easily.Notes:
- All pulses to be counted are to be TTL compatible. They should not exeed 5V and not fall below ground.
- You can add more digits by building a second (or third, or fourth, etc...) circuit and connecting the pin 11-6 junction of the 74LS90 and 74LS47 to pin 14 of the 74LS90 in the other circuit. You can keep expanding this way to as many digits as you want.
Stereo Tone Control using LM1036

This a stereo tone control circuit built using LM1036 IC. This control circuit bass / treble tone level, volume and balance between the right channel and left channel (Input 1 and 2). You can use this circuit for stereo applications such as car radio, television and audio systems, MP3 player, DVD player, ipod and more. An additional control input allows loudness compensation to be made simply. The circuit must be working with a supply voltage of 9V to 15V DC.
Each tone response is defined by a single capacitor chosen to give the desired characteristic. By changing the values of capacitors connected to the tone control unit, you can control bass and treble levels. pin 3 and pin 18 of IC are for acute and pin 6 to pin 15 for bass.
Each tone response is defined by a single capacitor chosen to give the desired characteristic. By changing the values of capacitors connected to the tone control unit, you can control bass and treble levels. pin 3 and pin 18 of IC are for acute and pin 6 to pin 15 for bass.
Tuesday, November 1, 2011
Home Telephone FM Transmitter Circuit
Here the schematic diagram of home telephone FM transmitter. This circuit connects in series with your home phone line and delivers the phone conversation through the FM band any time you pick up the telephone handset. Transmitted signal could be tuned by any FM receiver. The circuit features an "On Air" LED indicator and also gives you a switch that can be utilized to turn off the transmitter. A special characteristic of the circuit is the fact that no battery is required to operate the circuit because electrical power is taken from your phone line.
The transmitter circuit works by using only a short piece of wire aerial about 4" / 10 cm long to transmit the signal and a portion of the RF signal can also be radiated via the phone line itself. The circuit may possibly be implemented to share or record conversations, but will not be meant for illegal use.
Source: Home Telephone FM Transmitter Circuit
Thursday, October 27, 2011
Doorbell Sound with CD4001 CD4060
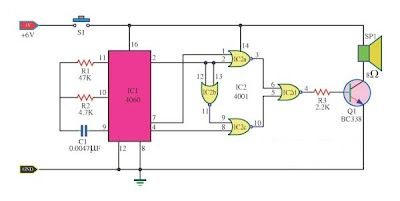
The doorbell sound circuit was two-tone sound. With the switch S1. working of the circuit, IC1 is a frequency division circuit, and a sound frequency generator came out.by C1, R1 is the frequency generator.
This audio signal from pin 7 and pin 4 to pin 1 and pin 8 of the IC2a, IC2c respectively. The IC2b of a frequency converter to control IC2c.When control signal during the low (Low) 1.25 kHz frequency coincides with IC2a.At same time, the control signal is in a high state IC2b (high) , 300 Hz frequency IC2c parties. Output on pin 3 of low IC2a under the same conditions, production and IC2c IC2a IC2d.Which is sent to act as a signal and the output transistors act as switches Q1 and tones amplifiers.The can be heard as two strokes. R3 acts as a volume, add more value to make the softest sound, but softer, a source of 6 volts.
This audio signal from pin 7 and pin 4 to pin 1 and pin 8 of the IC2a, IC2c respectively. The IC2b of a frequency converter to control IC2c.When control signal during the low (Low) 1.25 kHz frequency coincides with IC2a.At same time, the control signal is in a high state IC2b (high) , 300 Hz frequency IC2c parties. Output on pin 3 of low IC2a under the same conditions, production and IC2c IC2a IC2d.Which is sent to act as a signal and the output transistors act as switches Q1 and tones amplifiers.The can be heard as two strokes. R3 acts as a volume, add more value to make the softest sound, but softer, a source of 6 volts.
Class A MOSFET Amplifier 2SK1058

This is simple class A MOSFET amplifier 2SK1058 used in the circuit. It is easy to do, you should use a 24V supply volt at high current. using amplifier with Class A tube preamp based on 12AU7. It produces the purest sound. I have no idea of the levels of distortion, but has a very fine and delicate texture quality. With only one watt speaker output should be used efficiently. Lower is better than expected and the stage design of the units of my 12 "base 63L 3-way speakers with ease.
Monday, October 10, 2011
Battery Charger using LM317 Regulator
This Battery Charger is very similar to the universal charger that uses the constant current load. But this is much simpler to build and can be built using only two parties, the LM317 regulator and resistance. The use of diode D is for protection against short circuits. Capacitors C1 and C2 is good voltage regulation. Resistance R2 operates a dummy load when the battery is disconnected. The idea of this magazine is the output current is equal to 1.2 V, divided by the value of R1.
Part List:
LM317
R1 - see the values in table below
R2 - 2.2 kilo-ohms 1/4W
C1,C2 - 47uF/25V, or any value will do, the higher the better
D - 1N4001 or any similar diode at-least 1A rated
Part List:
LM317
R1 - see the values in table below
R2 - 2.2 kilo-ohms 1/4W
C1,C2 - 47uF/25V, or any value will do, the higher the better
D - 1N4001 or any similar diode at-least 1A rated
1,5V Simple FM Transmitter
This simple FM (frequency modulation) transmitter is powered only by a 1.5V battery and uses only one frequency of this transmitter transistor.The is controlled by the LC resonant circuit and operates from 80 to 110 MHz
The inductor L1 is 8 turns of wire wound magnetic No. 22 with diameter of 4 to 5 cm or the diameter of a pencil. The antenna is a 6-inch cable connected to the copper half of the L1 inductor.Other parts are not critical and can be replaced by their nearest value. Resistance 1 / 4 watt ceramic capacitor type and, except for electrolytic capacitor 10uF. 5-60pF capacitor is a type of court or variable rate.
The inductor L1 is 8 turns of wire wound magnetic No. 22 with diameter of 4 to 5 cm or the diameter of a pencil. The antenna is a 6-inch cable connected to the copper half of the L1 inductor.Other parts are not critical and can be replaced by their nearest value. Resistance 1 / 4 watt ceramic capacitor type and, except for electrolytic capacitor 10uF. 5-60pF capacitor is a type of court or variable rate.
Saturday, September 24, 2011
80W Power Amplifier Circuit
80W power amplifier circuit diagram based MJL4281A / MJL4302A and MJE15034 / MJE15035 power transistor. Actually the output power range is about 60W to 80W. This is an incredibly excellent amplifier. It's easy to construct, applies generally offered parts and is stable and well-performing. The diagram featured is really a full update on the original project, and even though it has a lot of similarities, is definitely a different design.
This amplifier circuit, even though extremely simple, is capable of great performance. This is not an amp to be under estimated, as the sonics are pretty good indeed, and this really is due (in part, at least) to the inherent simplicity of the diagram design. The amplifier is exceptionally quiet, and is reasonably tolerant of hard loads. It's an perfect amplifier for biamped systems, and may possibly be operated in bridge mode (BTL) in case you apply the suggested output transistors (which have the required power ratings).
Go to this 60-80W power amplifier page to get the detailed information about the circuit.
Tuesday, September 20, 2011
50MW Audio Amplifier circuit
The following is a small audio amplifier comparable to what you may come across a small transistor radio medium size. The input stage is biased to ensure that the power is divided equally to provide the two complimentary output transistors which are slightly biased in conduction of the diodes between the bases. A 3.three ohm used in sequence for the use of the issuers of the output transistors to stabilize the bias current that does not change significantly with temperature or several transistors and diodes.
Due to recent increases in bias voltage between the emitter and base decreases as a result of minimizing driving. Input impedance is 500 ohms and the voltage gain is approximately five to eight ohm speaker connected. The voltage swing around the speaker is 2 volts without distorting production and capacity is at the same time in the 50 milliwatt range. A high voltage provided as well as the addition of heat sinks in the output transistors would be a great source of more power. Circuit thirty milliamperes draw a supply of 9 volts.
Due to recent increases in bias voltage between the emitter and base decreases as a result of minimizing driving. Input impedance is 500 ohms and the voltage gain is approximately five to eight ohm speaker connected. The voltage swing around the speaker is 2 volts without distorting production and capacity is at the same time in the 50 milliwatt range. A high voltage provided as well as the addition of heat sinks in the output transistors would be a great source of more power. Circuit thirty milliamperes draw a supply of 9 volts.
300W MOSFET Broadband Amplifier
The back scheme will provide the best Motorola for any MRF141G typical application (including the functions of stabilization parasites), a power of broadband RF MOSFET put a conservative 300 watts rated through the broadcast band FM. The flange on the MRF141G be mounted on a heat sink, a copper plate 5 / 16 "thick and 6" x 8 ", which is mounted to the heat sink with 6-32 machine screws in the case that the heat sink is drilled and exploited.
CAUTION: This amplifier operates at very high energy ranges. You could receive significant RF burns if it comes in contact with open coaxial power of the amplifier. Also, if your transmitting antenna is mounted on the ceiling, and it should fly in a wind storm despite eating all the power of this amplifier, you can start a fire in certain types of roofing insulation! Be very careful with the use, installation and operation of the unit.
CAUTION: This amplifier operates at very high energy ranges. You could receive significant RF burns if it comes in contact with open coaxial power of the amplifier. Also, if your transmitting antenna is mounted on the ceiling, and it should fly in a wind storm despite eating all the power of this amplifier, you can start a fire in certain types of roofing insulation! Be very careful with the use, installation and operation of the unit.
Saturday, September 17, 2011
Rain Detector Circuit Using NE555
Rain detector using In principle it is an astable multivibrator 555, which is prepared by IC555 with a sensor attached that can detect water. Astable multivibrator with the 555 is in the audio frequency with a frequency of 1 KHz. The use of rain detector circuit can be disupplay 555 with voltage source that is free enough as 5 to 15 VDC. In the application of rain detector circuit The use of this object 555 can be mounted engine, car and others who want to protect from rain.
Water sensor used in the rain detector circuit 555 Using this you can do yourself a PCB Degan make the path as shown in the image above or, as described from the image above is the use foil glued to a board or boards that are plastic insulation. The important principle of this sensor is to conduct electrical current very well when the surface is exposed to water even a little.
Thursday, September 15, 2011
10 Band Graphic Equalizer Circuit

This 10 Band Graphic Equalizer Circuit a single chip, IC TL074 to achieve a 5-band graphic equalizer for use in systems of high fidelity audio. The 5-band graphic equalizer is true for radio-cassette player and car stereos. This unit features: low distortion, low noise, wide operating voltage range (3.5 V to 16V), low consumption (5 mA), Wide Dynamic Range (SD = 2.1Vrms/VCC = 8V) and built an amplifier input and output buffer.
The TL074 is a five-point graphic equalizer that has integrated all the functions necessary for a cochlear implant. The IC is the system of five sounds and control input and an output buffer amplifier. The following PDF contains detailed information on the wiring diagram for the 5-band graphic equalizer with a single IC / chip (BA3812L). The circuit shown in the table of works about five frequency bands: 100 Hz, 300 Hz, 1 kHz, 3 kHz, 10 kHz.
CMoy Headphone Amplifier Circuit
The following diagram is the circuit of CMoy headphone amplifier. Chu Moy designed a very popular headphone amplifier that’s easy to build, and it can be built small enough to fit in a pocket, power supply and all. It’s powerful enough to drive very inefficient headphones to thunderous volumes from even weak sources
CMoy headphone amplifier circuit diagram:
The op-amp used for this circuit is OPA2132PA, you may use OPA2132P or OPA2134PA as the alternative op-amp chip.
Power supply circuit for CMoy headphone amplifier:
Go to this page for the complete tutorial of CMoy headphone amplifier circuit.
ReadMore[..]
CMoy headphone amplifier circuit diagram:
The op-amp used for this circuit is OPA2132PA, you may use OPA2132P or OPA2134PA as the alternative op-amp chip.
Power supply circuit for CMoy headphone amplifier:
Go to this page for the complete tutorial of CMoy headphone amplifier circuit.
Wednesday, September 14, 2011
FM Transmitter circuit using 2N2222
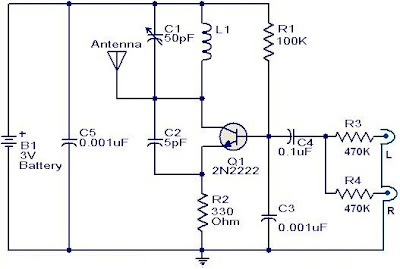
The FM transmitter circuit is using NPN transistor 2N2222. The L1 and C1 producess necessary oscillations Q1.The collector capacity C4, R3 and R4 resistor performs the function of the output mix theaudio to stereo player or i-emitter resistor R2 Pod.The provides sufficient stability for circuit.It also limits the collector current increse the battery.
With this circuit compact FM adapter connected to the audio output of your cassette player or i pod words, you can listen to your favorite music on the car track is stereo.This doesnot handy if your car stereo has an auxiliary circuit outlet is not to buy a short-range FM transimitter.
Sunday, September 11, 2011
RE46C190 Photoelectric Smoke Detector

This photoelectric smoke detector can be Created a very simple and low power smoke detector alarm that is based on the RE46C190 smoke detector IC. With a minimum of external components, this circuit alarm smoke detectors are provided all the necessary features for a project type photoelectric smoke detector address.
The design incorporates a selectable gain amplifier photos for use with a pair of infrared emitter detector. A flash power internal oscillator circuit smoke detector every 10 seconds, to keep the standby current to a minimum. If smoke is sensed, the detection rate is higher for verifying an alarm condition.
The design incorporates a selectable gain amplifier photos for use with a pair of infrared emitter detector. A flash power internal oscillator circuit smoke detector every 10 seconds, to keep the standby current to a minimum. If smoke is sensed, the detection rate is higher for verifying an alarm condition.
AM Portable Receiver Using ZN414

a AM portable radio receiver using ZN414 IC. The ZN414 ic has now been replaced by the MK484 which is identical in performance and pinout.
Designed around the popular ZN414 IC this receiver covers the range of medium wave band of approximately 550 to 1600 KHz with the values indicated. The condenser coil and tuning can be taken from an old MW radio to save time. The ZN414 IC, has been replaced by the MK484. The integrated circuit is a 3 pin, tuned circuit radio frequency, and incorporates several RF stages, automatic gain control and an AM detector. It's easy to overload and voltage of th IC is critical to success.
In this circuit a small voltage regulator turns on the transistor BC108B, 1N4148 diodes four, 2k7 and 10k resistor and the resistance of pre 820R. The 10k pot control acts as a receptor selectivity for all, control the operating voltage for the ZN414 (or MK484).
The audio amplifier is built on an investment of 741 op-amp amplifier circuit. Additional current pulse is provided by the BC109C / BC179 complementary pair of transistors to drive a 8 ohm speaker. The voltage gain full audio amplifier is around 15. The audio output of the complete receiver is really good and undistorted.
Designed around the popular ZN414 IC this receiver covers the range of medium wave band of approximately 550 to 1600 KHz with the values indicated. The condenser coil and tuning can be taken from an old MW radio to save time. The ZN414 IC, has been replaced by the MK484. The integrated circuit is a 3 pin, tuned circuit radio frequency, and incorporates several RF stages, automatic gain control and an AM detector. It's easy to overload and voltage of th IC is critical to success.
In this circuit a small voltage regulator turns on the transistor BC108B, 1N4148 diodes four, 2k7 and 10k resistor and the resistance of pre 820R. The 10k pot control acts as a receptor selectivity for all, control the operating voltage for the ZN414 (or MK484).
The audio amplifier is built on an investment of 741 op-amp amplifier circuit. Additional current pulse is provided by the BC109C / BC179 complementary pair of transistors to drive a 8 ohm speaker. The voltage gain full audio amplifier is around 15. The audio output of the complete receiver is really good and undistorted.
Thursday, September 8, 2011
4 Channel Audio Mixer using LM381
 4 channel audio mixer using the LM381 IC low noise dual preamplifier. Each of the two amplifiers is completely independent lm381, with each internal power supply decoupler-regulator with 120 dB of rejection of the offer and 60 dB channel separation. Other features include high gain (112 dB), large output voltage swing (VCC b 2V) pp and wide power band width (75 kHz, 20 Vp-p).
4 channel audio mixer using the LM381 IC low noise dual preamplifier. Each of the two amplifiers is completely independent lm381, with each internal power supply decoupler-regulator with 120 dB of rejection of the offer and 60 dB channel separation. Other features include high gain (112 dB), large output voltage swing (VCC b 2V) pp and wide power band width (75 kHz, 20 Vp-p).High gain operational amplifier combines four individual input signals. The DC power supply should be well filtered, and the circuit must be protected to avoid picking up hum. If you need more audio inputs that can add more inputs by connecting another capacitor 1uF in series with a 500k pot to the network.
To supply the project audio mixer electronic circuit can use a DC power supply (or battery) that will provide an output voltage between 9 and 24 volts.
120W Stereo Amplifier using STK4241V

Here is a circuit 120 watt stereo amplifier using STK4241V. The MAX9710 a stereo audio power amplifier capable of delivering 2 x 120 W of the IC to put loads of 8 ohms. MAX9710 can be operated from ± 32V single power supply of ± 54V.
This amplifier circuit is ideal for audio devices for home supply. STK4241V amplifier specifications might lead one to believe that you can use supply voltages of ± 78V. With zero input signal (and therefore no way out) I could, but I would not recommend anything better than ± 45V 8-ohm loads, if expected, although ± 54V will be fine if you can provide a good heat sink.
This amplifier circuit is ideal for audio devices for home supply. STK4241V amplifier specifications might lead one to believe that you can use supply voltages of ± 78V. With zero input signal (and therefore no way out) I could, but I would not recommend anything better than ± 45V 8-ohm loads, if expected, although ± 54V will be fine if you can provide a good heat sink.
Monday, September 5, 2011
Multi-color LED Driver Schematic
Have you ever wondered how many various colours can illuminate a LED? One, two or possibly three? Making this simple circuit, you will discover it a lot more. The important component in this design is a dual LED. One such accessory includes two inside the 'slices' of different diode LED, that each and every of them produces a different color (commonly green and red). For the drive needs three pins, a common cathode and two separate roots. In this way every single of the two integrated diodes can light up as independent of one another. You'll find only two colors that may create this dual LED.
Setting appropriate percentage of the currents flowing via two separate channels of the POY is, we have other from pure green and red, orange (IR = 21G) and yellow (IG = 2IR). In this circuit, the anodes of the double LED driven by the outputs a six-point buffer tri-state technology CMOS. As opposed to most integrated family of CMOS 4000, the 4503 applied here, can supply many different loads on high currents of the order of 10 mA. The stream that goes towards the two diodes is limited by the resistors R1 to R6 whose specific values are those that attain the distinct colors and changing brightness them. The circuit was originally created to display three various situations, each expressed their the presence of logical '1 'in one of the inputs a, b, c. The entries are able to activate only one of every single time, and if none of them had been excited, a NAND gate (IC1c) ensured that the LED 'to create fourth color. In the improved version we present these days, the circuit has added another level oscillator (IC 1 a and IC1b), which produces about two pulses per second. The pulses are introduced in the entrance activation OA (pin 1) of 4503, resulting in colorful flashes. The oscillator is controlled by the of logical statements applied to the inputs 'd' and 'e'. If both are simultaneously logical '1 ', then each the oscillator and also the buffers of 4503 stay inoperative. If e = 1 and d = 1, then all buffers are driven in a state of high resistance plus the circuit absorbs the least feasible electric current (standby). The power supply circuit was initially set at 12 Volt, but all of the components that are able to work equally properly with any voltage in between 5 Volt and 16 Volt.
Thursday, September 1, 2011
UPC1651 FM Transmitter

Here is the circuit of an FM transmitter with the IC UPC1651. UPC1651 is a broad band amplifier MMIC UHF silicon. The IC has a wide frequency response and power to win up to 1200MHz 19dB.The IC can be operated at 5V DC.
The audio signals picked up by the microphone is fed to the input terminal (pin 2) of the IC through the capacitor C1. C1 acts as a noise filter. The FM modulated signal will be available at the output pin (pin 4) of the IC. L1 inductor and capacitor C3 LC circuit forms necessary for the creation of the oscillations. Transmitter frequency can be varied by adjusting the capacitor C3.
Notes.
The circuit can be assembled on a Vero board.
Inductor L1 can be made by making 5 turns of 26SWG enameled copper wire on a 4mm diameter plastic former.
A ¾ meter insulated copper wire can be used as the antenna.
Do not give more than 6V to the IC.
Mic M1 can be a condenser microphone.
The audio signals picked up by the microphone is fed to the input terminal (pin 2) of the IC through the capacitor C1. C1 acts as a noise filter. The FM modulated signal will be available at the output pin (pin 4) of the IC. L1 inductor and capacitor C3 LC circuit forms necessary for the creation of the oscillations. Transmitter frequency can be varied by adjusting the capacitor C3.
Notes.
The circuit can be assembled on a Vero board.
Inductor L1 can be made by making 5 turns of 26SWG enameled copper wire on a 4mm diameter plastic former.
A ¾ meter insulated copper wire can be used as the antenna.
Do not give more than 6V to the IC.
Mic M1 can be a condenser microphone.
15W Stereo audio Amplifier using TDA 4935

TDA4935 2x15W audio amplifier is high quality Siemens IC. The IC can be used in stereo or bridge mode. In stereo mode can deliver 15W Stereo audio Amplifier using TDA 4935 per channel in bridge mode can deliver 30W to an 8 ohm load at the source of 30V. TDA4935 requires very few external components and has an ample supply voltage range. The IC operates in class B and has built-in protection circuits over temperature and overload protection.
Notes :
- The circuit must be assembled on a good quality PCB.
- TDA 4935 must be fitted with a proper heat sink.
- The supply voltage can be anything between 8 to 30V DC.
- Capacitors C1, C2, C8 are polyester capacitors.
- Capacitors C3, C4 and C6 are ceramic capacitors while C5 and C9 are electrolytic.
Saturday, August 27, 2011
5V Boost Converter using LTC3440
 A simple 5V boost converter using LTC3440 shown here. LTC3440 is a high efficiency DC to DC converter that can be operated from input voltages below, above or equal to the output voltage. As for the synchronous rectification, LTC3440 delivers up to 96% efficiency and up to 600 mA output current is guaranteed. The IC has built an oscillator whose frequency synchronized whose frequency can be adjusted from 300 kHz to 2 MHz
A simple 5V boost converter using LTC3440 shown here. LTC3440 is a high efficiency DC to DC converter that can be operated from input voltages below, above or equal to the output voltage. As for the synchronous rectification, LTC3440 delivers up to 96% efficiency and up to 600 mA output current is guaranteed. The IC has built an oscillator whose frequency synchronized whose frequency can be adjusted from 300 kHz to 2 MHzThe LTC3440 circuit is connected as a boost converter capable of delivering 5V output 5V @ 300mA constant input voltage of 2.7 to 4.2 V. The resistor R4 is used to set the oscillator frequency, while the resistors R1 and R2 are used to adjust the output to 5 volts. Resistance R3 and capacitor C1 form a frequency compensation network, while C3 serves as an input bypass capacitor. S1 is the stop switch and capacitor C2 is the output filter.
Metronome Generator Circuit using NE555
 Here is a simple circuit with NE555 IC that can be used to generate metronomes.Such circuit is very useful for those who learn music. The circuit is simply an astable multivibrator NE555 cable around. The components R1, R2 and C1 determine the frequency
Here is a simple circuit with NE555 IC that can be used to generate metronomes.Such circuit is very useful for those who learn music. The circuit is simply an astable multivibrator NE555 cable around. The components R1, R2 and C1 determine the frequencyNotes.
- The circuit can be wired on a general purpose PCB or common board.
- The circuit can be powered from a 9V PP3 battery.
- The POT R1 can be used to adjust the rhythm of the sound.
- The POT R2 can be used as volume control.
- The speaker k1 can be a n 8 Ohm tweeter.
Thursday, August 25, 2011
Static 0 to 9 Display using SN7446 and 7490

The circuit shown here is a simple Static 0-9 Display can be used in many applications. The circuit is based on 7490 asynchronous decade counter (IC2), a 7-segment display (D1), and a seven-segment decoder / driver IC 7446 (IC1).
The seven-segment display consists of 7 LEDs as 'a' to 'g'. For different LEDs bias, we can show the digits 0 to 9. Seven Segment Displays are of two types, the common cathode and common anode. Like the type of anode anodes of all seven LEDs are attached, while the type common cathode cathodes are all together. The seven-segment display used here is a type common anode. The resistance R1 to R7 are current limiting resistors. IC 7446 is a decoder / driver IC that is used to control the seven segment display.
Work of this circuit is very simple. For each clock pulse output of IC2 BCD (7490) advances a bit. The IC1 (7446) decodes the BCD output for the form of seven segments and controlling the display to indicate the corresponding digit.
The seven-segment display consists of 7 LEDs as 'a' to 'g'. For different LEDs bias, we can show the digits 0 to 9. Seven Segment Displays are of two types, the common cathode and common anode. Like the type of anode anodes of all seven LEDs are attached, while the type common cathode cathodes are all together. The seven-segment display used here is a type common anode. The resistance R1 to R7 are current limiting resistors. IC 7446 is a decoder / driver IC that is used to control the seven segment display.
Work of this circuit is very simple. For each clock pulse output of IC2 BCD (7490) advances a bit. The IC1 (7446) decodes the BCD output for the form of seven segments and controlling the display to indicate the corresponding digit.
6V Gel Cell Charger Circuit
This is the diagram of 6V Gel Cell charger. The circuit is using NE555 timer as oscillator and TPI31T switching transistor. The schematic diagram designed by Tony Van Roon.
Parts List:
| R1 = 22 ohm, 1W R2 = 270 ohm R3 = 220 ohm *R4 = 715 ohm, 1% *R5 = 3.57K, 1% *R6 = 1.40K, 1% *R7 = 1.47K, 1% | C1 = 100nF C2 = 100nF D1 = 1N4001 T1 = TIP31A, B, C (or equivalent) U1 = Timer IC NE555V (or equivalent) S1 = Toggle switch, ON-OFF |
6V Gel Cell Charger circuit source page
Sunday, August 21, 2011
Lamp Flasher using IC LM395

This circuit of powerful flashing lamp is good use in vehicles. The LM395 IC based on circuit also known as super-transistor, which is terribly powerful integrated monolithic power transistor with options such as thermal protection, current limit etc. In fact, this circuit is almost indestructible.The IC will handle currents up to 1A 40V and switch in less than 500 nanoseconds. Resistor R1 and capacitor C1 determine the frequency of blinking. With the flash rate indicates the value is approximately 1 flash per second.
Saturday, August 20, 2011
Simple Circuit 12V to 120V DC DC Converter
 Its a simple circuit of 12V DC to 120V DC converter. The circuit consists of two phases first phase of the investor base and then a rectifier and filter stage. IC1 NE555 is wired as an astable multivibrator operating at a frequency of 100 Hz and can be adjusted to the preset R1. IC1 output is coupled to the clock input of IC2 is a dual CMOS D flip-flop. IC2 divides the pulse train of 100 Hz IC1 2 50 Hz pulse trains that are 180 degrees out of the party and offered on the pin 1 and 2 of IC2.
Its a simple circuit of 12V DC to 120V DC converter. The circuit consists of two phases first phase of the investor base and then a rectifier and filter stage. IC1 NE555 is wired as an astable multivibrator operating at a frequency of 100 Hz and can be adjusted to the preset R1. IC1 output is coupled to the clock input of IC2 is a dual CMOS D flip-flop. IC2 divides the pulse train of 100 Hz IC1 2 50 Hz pulse trains that are 180 degrees out of the party and offered on the pin 1 and 2 of IC2.When pin 1 is high transistor Q1 conducts and current flows through the upper half of T1 primary winding. When pin 2 is the transistor Q2 conducts and high current flows through the lower half of the primary coil T1. As a result of a voltage of 120 V AC are induced in the secondary of T1. This voltage is rectified with bridge D1 to provide a 120V DC output. Capacitor C2 is the DC input filter, while C3, C4 are the output filters.
Notes.
- The circuit can be assembled on a vero board.
- Q1 and Q2 require heat sink.
- Output power of this dc dc converter is around 100 watts.
- IC1 and IC2 are to be mounted on holders.
- An optional 5A fuse can be added in series to the 12V supply line.
- T1 can be a 9-0-9V /250V/3A mains transformer.
- If 3A bridge is not available make one using 1N5408 diodes.
- Out of the two Flip-Flops inside CD4013 only one is used here.
- Output of IC1 must be set to 100Hz by adjusting preset R1
Thursday, August 18, 2011
DC Motor Controller Circuit with NE555
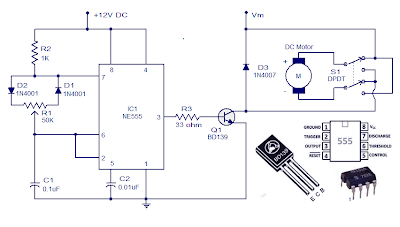
A simple DC motor controller circuit with NE555 is shown here. several DC motor speed control circuits are revealed here however this can be the first one using NE555 timer IC. additionally to controlling the motors speed its direction of rotation will be also modified using this circuit.
A PWM circuit primarily based on timer NE555 is that the heart of this circuit. NE555 is wired as an astable multivibrator whose duty cycle will be adjusted by varying the POT R1. The output of IC1 is coupled to the base of transistor Q1 that drives the motor according to the PWM signal available at its base. Higher the duty cycle the typical voltage across motor will be high which ends in higher motor speed and vice versa. modification of DC motor direction is attained using the DPDT switch S1 that on application simply toggles the polarity applied to the motor.
6-8A / 0-28V Variable Power Supply Circuit
This is the schematic diagram of variable power supply. The output voltage of this power supply circuit can be adjust from 0V to 28V DC, while the current output is static the rang is about 6A up to 8A.
Parts List:
| R1 = 2K2 Ohm 2,5 Watt R2 = 240 Ohm R3,R4 = 0.1 Ohm 10 Watt R7 = 6K8 Ohm R8 = 10K Ohm R9 = 47 Ohm 0.5 Watt R10 = 8K2 Ohm C1, C7, C9 = 47nF C2 = 4700uF/50v – 6800uF/50v C3, C5 = 10uF/50v C4, C6 = 100nF C8 = 330uF/50v C10 = 1uF/16v C11 = 22nF | D1…D4 = four MR750 diodes (MR750 = 6 Ampere diode) or 2 x 4 1N5401 diodes. D5 = 1N4148, 1N4448, 1N4151 D6 = 1N4001 D10 = 1N5401 D11 = LED D7, D8, D9 = 1N4001 TR = 2 x 15 volt (30volt total) 6+- Ampere IC1 = LM317 T1, T2 = 2N3055 P1 = 5k P2 = 47 Ohm or 220 Ohm 1 Watt P3 = 10k trimmer pot F1 = 1 Amp F2 = 10 amp |
Source: schematicdiagram.s4s.in
Monday, August 15, 2011
Doorbell circuit using NE555 IC

The main part of this circuit Doorbell two timer NE555 ICs.When someone hit the switch S1 momentarily, the speaker emits a sound of the bell, if the time period of the monostable multivibrator built around IC1.
When the switch S1 pressed, IC1 is enabled in your pin 2 and pin 3 output is high for a period of time previously set by the values of R4 and POT POT R5.When ofIC1 restores the IC2 output is high and starts to swing to make a bell sound through the speaker.The IC2 is configured as an astable multivibrator whose oscillation frequency can be varied with the help of POT R5.By adjusting the values of R4 and R5, changes in tone are possible
Notes.
- The circuit has to assembled on a good quality PCB or common board.
- The IC1 & IC2 has to be mounted on IC holders.
- Power the circuit from a 9V battery or 9V DC power supply.
- Switch S1 is push button switch.
Class B audio amplifier based on TDA1553

Here is the circuit of a Class B audio amplifier based on TDA1553. TDA1553 is a monolithic audio amplifier class B, containing 2 x 22 watt amplifier in bridge configuration load attached. The amplifier operates from 12V DC and develops intentionaly for car audio applications. The IC also has a lot of good features such as short circuit protection, protection of the load dump, reverse polarity protection, speaker protection, etc.
In the circuit, C5 and C4 are decoupling capacitors C3 input, while setting the delay for speaker protection. C1 and C2 are filter capacitors of the offer.
Notes :
- Assemble the circuit on a good quality PCB.
- Use 12V DC for powering the circuit.
- The circuit can deliver 22W per channel into 4 ohm speakers.
- Fit the IC with a proper heat sink.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)